In our previous analysis of popular projects, we discussed Polygon’s AggLayer, which is quite similar to Paralism’s Protocol-Agnostic concept. Both are exploring how to aggregate existing blockchains, users, and liquidity to form a unified entry point into Web3, thereby breaking down the isolated ecosystems barriers.
Continue reading The Aggregation of Web3.0: Protocol-Agnostic and AggLayerCategory: Research and opinion
Overview of Web3.0 Fundraising in August
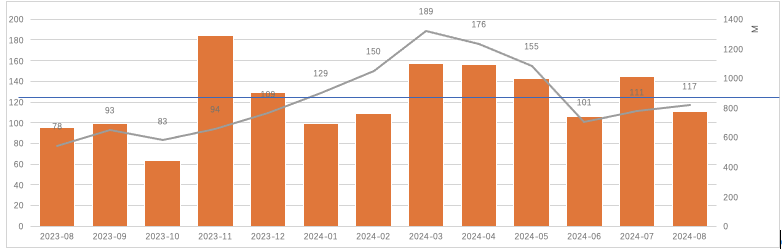
In August 2024, Web3.0 projects completed a total of 117 financing rounds, raising approximately $777 million, which is lower than the monthly average over the past year (around $867 million, shown by the blue line in the chart below). The market experienced significant fluctuations in August, and the capital market was also affected. However, the situation is still better compared to the same period last year.
Popular Project Analysis: Polygon
On August 22, Polygon announced that it will upgrade its mainnet on September 4 and migrant its native token Matic to POL. Subsequently, several major exchanges announced their support for this upgrade, delisting Matic and listing POL. As a result, Polygon has once again come into the public eye. Over the past year, BTC rose from over $20,000 to over $70,000 at its peak, while Matic increased from over $0.50 to $1.20 but has recently fallen below $0.50. As an Ethereum Layer 2 solution dedicated to addressing scalability issues, Polygon’s past achievements are undeniable. Even during the bear market of 2022 and 2023, it saw the second-largest increase in developer numbers just after Ethereum.
So, let’s take this opportunity to study Polygon once again.
Continue reading Popular Project Analysis: PolygonOverview of Web3.0 Fundraising in July
In July 2024, Web3 related projects secured a total of 113 funding rounds, with the total amount raised exceeding $1.1 billion USD, almost equals to the monthly average of the first half of the year. However, compared to July of the previous year, both the funding amount and the number of rounds has significantly increased. In fact, since last November, the overall fundraising environment for the Web3.0 market has notably improved, maintaining a relatively stable state this year.
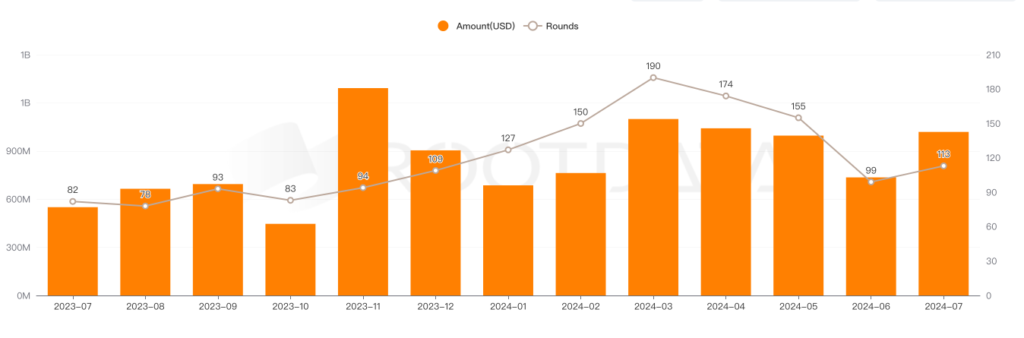
Data resource: https://www.rootdata.com/dashboard
Continue reading Overview of Web3.0 Fundraising in JulyAnalysis of MegaETH
On this June 27th, the Layer 1 project MegaETH, developed by MegaLabs, completed a $20 million seed funding round with a valuation of at least $100 million. The round was led by Dragonfly, with participation from Figment Capital, Robot Ventures, Big Brain Holdings, and others. Angel investors included Vitalik Buterin (co-founder of Ethereum), Joseph Lubin (founder of ConsenSys), Sreeram Kannan (founder of EigenLayer), Kartik Talwar (ETHGlobal co-founder), Mert Mumtaz (Helius Labs co-founder), Santiago Santos, Hasu, and Jordan Fish (Cobie), etc. Why does MegaETH attract support from key figures in the Ethereum ecosystem like Vitalik? What significance does it hold for the Ethereum ecosystem? Let’s check it out together.
What is MegaETH?
MegaETH describes itself as the “first real-time blockchain.” The team analyzed the difficulties and bottlenecks faced by existing Layer 2 solutions in improving performance and provided specific, detailed solutions. In simple terms, MegaETH aims to enhance blockchain performance through a heterogeneous blockchain architecture and a “Hyper-optimized” EVM execution environment, and pushes throughput, latency, and resource efficiency to hardware limits Their final goal is to achieve a TPS of over 100k/ and block production speeds of less than 1ms.
MegaETH’s Solutions
Node Specialization
In Layer 1, all nodes are homogeneous, performing the same tasks. While layer 2 is inherently heterogeneous, allowing different nodes to specialize in specific tasks. MegaETH takes one step further by decoupling the task of transaction execution from full nodes: Sequencer nodes handle transaction ordering and execution; full nodes manage state updates and verification, and proof nodes validate blocks. This key architectural decision allows MegaETH to significantly enhance network performance, while minimizing the hardware requirements for full nodes.
Real-Time EVM
MegaETH has also optimized the transaction execution. Parallel EVM is currently a popular method for processing large volume transactions, as seen in projects like Monad we talked earlier. However, MegaETH’s research reveals that the median parallelism in recent Ethereum blocks is less than 2. Even with artificial merging blocks into large batches, the median parallelism only increases to 2.75. This indicates that most transactions are interdependent, making it impossible to significantly improve transaction execution speed through parallelism alone.
MegaETH enhances the current parallel processing speed by a transaction-priority optimized parallel algorithms (streaming-based block building). We haven’t seen a more detailed description of this yet; if more information revealed later, we will share it with you.
In-Memory COMPUTATION
Thanks to node specialization, MegaETH’s sequencers are equipped with ample RAM to store the entire EVM state and state trie in memory, resulting in a 1000x increase in state access speed compared to SSD-based systems. Additionally, high-end servers with 1-4 TB of memory are readily available in the cloud, providing ample state for future growth.
This approach is known as in-memory computing in Web2, and by introduce it into blockchain, we will able to support high-performance, data-intensive Web2 applications than ever.
Smart Contract Compilation
MegaETH employs Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation to translate smart contracts into native machine code on the fly, improving the efficiency of interpreting EVM bytecode and simulating stack machines. While most contracts may see limited performance improvements in production, compute-intensive applications could see up to a 100x performance boost, making MegaETH ideal platform for sophisticated DApps requiring real-time performance.
Optimized State Trie Updates
State trie update speed is the largest bottleneck for EVM-compatible blockchains due to intensive disk I/O operations. MegaETH addresses this by replacing the Merkle Patricia Trie (MPT) with a new state trie designed from scratch. This new trie minimizes disk I/O operations and scales efficiently to terabytes of state data while maintaining full EVM compatibility
State Sync Protocol
MegaETH employs an efficient peer-to-peer protocol to update the state from sequencers to full nodes with low latency, ensuring even nodes with modest internet connections remain synchronized with the latest state, capable of handling updates at a rate of 100,000 TPS.
Summary

MegaETH appears to be a highly technical team, offering a comprehensive solution to existing EVM problems and bottlenecks through specialized nodes, transaction parallelization, I/O state optimization, gas limit improvements, and more. Their approach provides a detailed and convincing solution to these issues, setting them apart from other projects that focus on optimizing only specific aspects.
Someone asked the founder of MegaETH, since they have done so many optimizations, why not issue a new blockchain? The answer is that their solution is based on outsourcing security and censorship resistance to the third party which are Ethereum and EigenLayer. What they aim to do is to enhance the performance of the EVMs. This is good news for the Ethereum ecosystem, and could be one of the main reasons Vitalik, who also has a technical background and also proposed the idea of node specialization before, supports MegaETH. Furthermore, with the biggest Ethereum’s ecosystem, user and funding are not major issues. However, this could also be MegaETH’s bottleneck. Can the 100,000+ TPS meet the needs of projects from Web2? It might be sufficient now, but more aggressive solutions might be required in the future.
MegaETH’s public testnet is expected to launch in early autumn, with the mainnet anticipated by the end of the year. We will keep you updated.
References: https://megaeth.systems/